Accession Data:
Rumex acetosa L.
- Common Name: Garden Sorrel, Sour Dock
- Family: Polygonaceae Juss.
- Description: The leaf of this herb has many uses. In cooking you can add raw leaves to sorrel soup or salads. You can cook Sorrel in the same manner as spinach for seasoning vegetable soups, lamb, beef, omelettes and sauces.
- Uses: Edible: Leaves - raw or cooked. They make a thirst-quenching on their own, or can be added to salads, used as a potherb or pureed and used in soups. A delicious lemon-like flavour, liked by most people who try them, they can be rather overpowering in quantity and are more generally used as a flavouring in mixed salads. The leaves can also be dried for later use. The leaves can be available all through the winter, especially in mild weather or if a little protection is given to the plants. The leaves should be used sparingly in the diet, see the notes on toxicity above. Flowers - cooked as a vegetable or used as a garnish. Root - cooked. It is dried, ground into a powder and made into noodles. Seed - raw or cooked. Ground into a powder and mixed with other flours to make bread. The seed is easy to harvest, but is rather small and fiddly to use. The juice of the leaves can be used as a curdling agent for milks.1
Medicinal: The fresh or dried leaves are astringent, diuretic, laxative and refrigerant. They are used to make a cooling drink in the treatment of fevers and are especially useful in the treatment of scurvy. The leaf juice, mixed with fumitory, has been used as a cure for itchy skin and ringworm. An infusion of the root is astringent, diuretic and haemostatic. It has been used in the treatment of jaundice, gravel and kidney stones. Both the roots and the seeds have been used to stem haemorrhages. A paste of the root is applied to set dislocated bones. The plant is depurative and stomachic. A homeopathic remedy is made from the plant. It is used in the treatment of spasms and skin ailments.1
- IMPORTANT NOTE: Plant Uses are for informational purposes only. EEB Greenhouses assume no responsibility for adverse effects from the use of any plants referred to on this site. Always seek advice from a professional before using any plant medicinally.
- USDA Zone: 3a-7b
Accession Data:
- Accession # 199200339
- Source: Steve Severson
- Accession Date: 12-31-1992
- Bench: 2315 - Lily Pond
- Currently: active - healthy
- Qty: 1 confirmed on 09-03-2024
- Restrictions:
- Poisonous Plant Parts - Not for Human Consumption
Small quantities are perfectly ok; large quantities should be avoided due to high levels of oxalic acid in leaves.
- Poisonous Plant Parts - Not for Human Consumption
Classification:
- Division: Magnoliophyta
- Class: Magnoliopsida
- SubClass: core eudicots
- Order: Caryophyllales
- SubOrder:
- Family: Polygonaceae
- SubFamily: Polygonoideae
- Tribe: Rumiceae
- SubTribe:
Flowering Data:
This accession has been observed in bloom on:| Year | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2024 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2023 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2022 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2021 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2020 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2019 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2018 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2016 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2015 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2012 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2011 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2010 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2008 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References (internal):
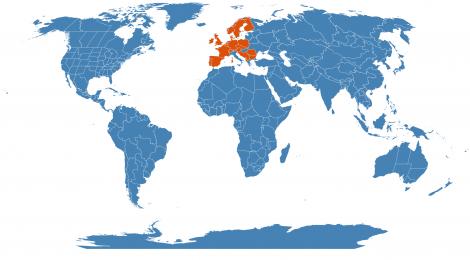
- EEB Greenhouse Holdings native to: Denmark / Finland / Great Britain / Ireland / Norway / Sweden / Austria / Belgium / Czechoslovakia / Germany / Netherlands / Poland / Switzerland / Corse / France / Portugal / Sardegna / Spain / Albania / Bulgaria / Romania / Yugoslavia
References (external):
- Plants For A Future Website
- The Plant List (2013). Version 1.1. Last accessed on Tuesday, November 01, 2016.
- Rumex acetosa at Wikispecies. Last accessed on Tuesday, November 01, 2016.
- Rumex acetosa at Global Biodiversity Information Facility. Last accessed on Tuesday, November 01, 2016.
data regenerated on Tue, 08 Oct 2024 12:01:30 -0400 [bcm v4.0]
Images:

Additional images for this accession:
Click on thumbnails to enlargeCurrent Accessions in the Polygonaceae
Subfamily Eriogonoideae
Subfamily Polygonoideae
Tribe Polygoneae
- Reynoutriinae: Fallopia aubertii
- Reynoutriinae: Homalocladium platycladum
- Reynoutriinae: Muehlenbeckia complexa

Subfamily Polygonoideae
Tribe Rumiceae
W/C = Wild Collected
 = indicates flowering in past 14 days
= indicates flowering in past 14 days
 = images available for this accession
= images available for this accession
 = map available for this accession
= map available for this accession
 = accession added within past 90 days
= accession added within past 90 days